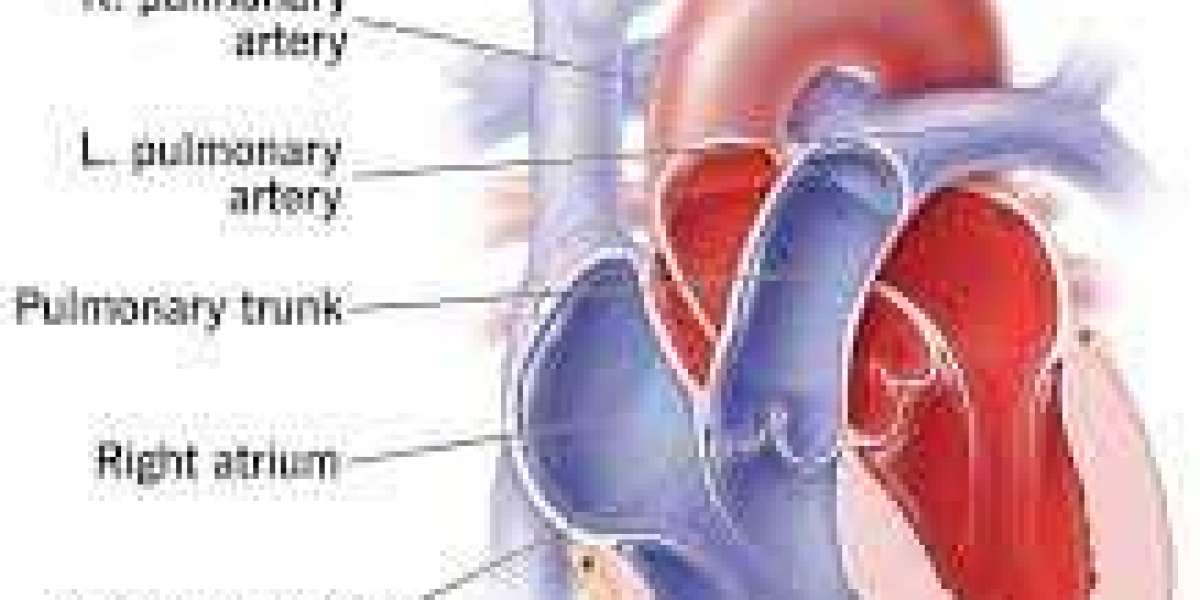
Pulmonary arterial health plays a crucial role in how our heart and lungs work together to deliver oxygen throughout the body. Though it may not be a term we hear every day, the pulmonary arteries are vital to our overall well-being. They carry blood from the heart to the lungs, where the blood picks up oxygen before circulating to the rest of the body.
In this blog, we’ll dive into what pulmonary arterial health means, what can go wrong, and why it’s essential to understand this part of the circulatory system—even if you’re not a medical professional.
What Is Pulmonary Arterial Health?
The pulmonary artery is a large blood vessel that starts at the heart’s right ventricle and branches into smaller arteries that go into each lung. These vessels are responsible for transporting oxygen-poor blood to the lungs. When they are functioning normally, blood flows freely and efficiently.
Good pulmonary arterial health means these arteries are strong, flexible, and free of blockages or damage. When issues arise in these arteries, it can affect your breathing, heart function, and overall energy levels.
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH)
One of the most serious conditions affecting the pulmonary arteries is pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). PAH is a type of high blood pressure that occurs in the arteries of the lungs. It can lead to heart strain and damage over time.
Common symptoms of PAH include:
Shortness of breath during routine activities
Fatigue and weakness
Chest pain or pressure
Dizziness or fainting spells
Swelling in the legs and ankles
The condition often develops slowly, making early diagnosis difficult. Left untreated, PAH can become life-threatening.
Causes of Pulmonary Arterial Problems
Several factors can contribute to poor pulmonary arterial health, including:
Genetic disorders
Autoimmune diseases like lupus or scleroderma
Congenital heart defects
Blood clots in the lungs
Certain medications and drugs
Sleep apnea or chronic lung diseases
Lifestyle and environmental factors such as smoking, a sedentary lifestyle, and long-term exposure to high altitude can also increase the risk.
Why Pulmonary Arterial Health Matters
Your lungs and heart work as a team. When the pulmonary arteries are damaged or narrowed, your heart has to work much harder to pump blood through them. This extra strain can lead to heart failure and decreased oxygen delivery to the rest of your body. That’s why it’s essential to monitor any signs of respiratory discomfort and seek medical help early.
Even body systems that seem unrelated can be impacted. For instance, when discussing overall blood circulation, people often ask, what does a boner feel like? Erections are directly tied to healthy blood flow, and poor circulation—resulting from something like PAH—can interfere with this natural process. It’s just one small example of how interconnected our vascular health truly is.
Diagnosis and Tests
Doctors use several tools to diagnose pulmonary arterial issues:
Echocardiogram: A non-invasive test that uses sound waves to check the heart’s function.
Chest X-rays and CT scans: These imaging tools help assess the size and condition of pulmonary arteries.
Right heart catheterization: A more invasive test that directly measures pressure in the pulmonary arteries.
Blood tests, physical exams, and exercise tolerance tests may also be part of the diagnostic process.
Treatment Options
While some causes of pulmonary arterial problems are not curable, many treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life:
Medications: Such as vasodilators, anticoagulants, diuretics, and oxygen therapy.
Lifestyle changes: Quitting smoking, eating heart-healthy foods, and regular low-impact exercise.
Surgical options: In severe cases, lung or heart-lung transplants may be considered.
Early detection and treatment are essential for slowing the progression of diseases like PAH and improving the patient’s outlook.
Final Thoughts
Pulmonary arterial health is essential for a strong cardiovascular and respiratory system. It affects how well your heart pumps, how your lungs function, and how your body gets the oxygen it needs. While the signs of trouble may be subtle at first, staying informed and proactive about your heart and lung health can make all the difference.
Whether you're managing a known condition or simply aiming for better wellness, understanding your pulmonary arteries is a step toward taking control of your health. Don’t ignore symptoms like fatigue, breathlessness, or chest discomfort—they could be early signs of a more serious issue. As always, consult your healthcare provider for guidance tailored to your unique health needs.