Introduction
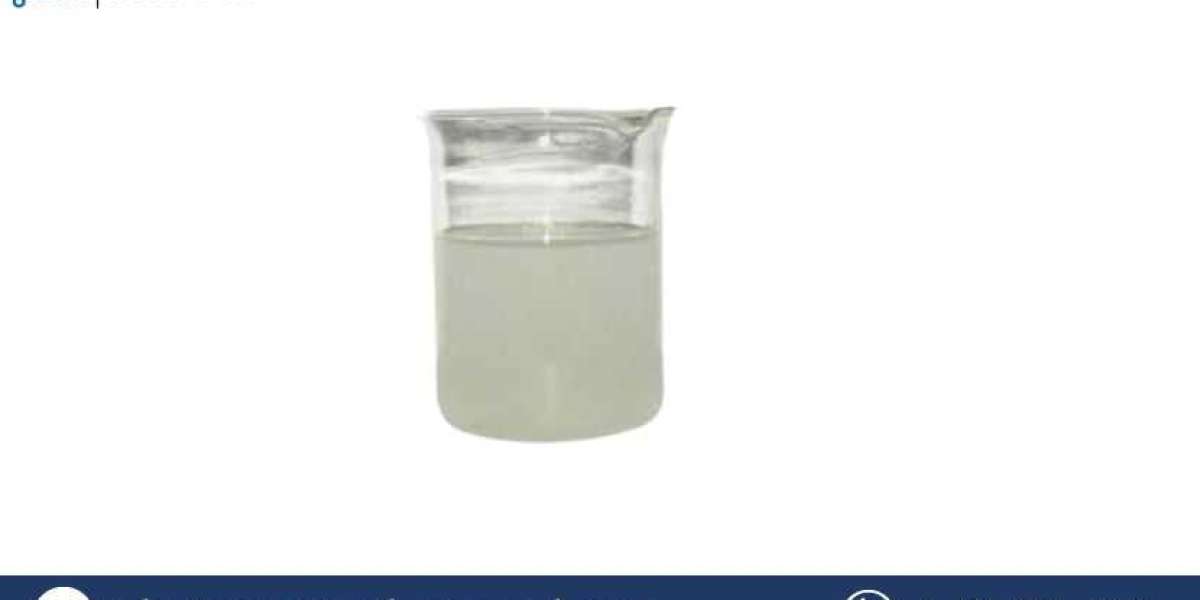
The Alkyl Ether Sulfates (AES) manufacturing plant project report is a comprehensive guide for setting up a facility that produces Alkyl Ether Sulfates, a class of anionic surfactants used extensively in personal care, household cleaning products, and industrial applications. Alkyl Ether Sulfates are primarily used in shampoos, body washes, detergents, and other cleaning products due to their ability to create a rich lather and their excellent cleansing properties.
This project report outlines the steps, processes, raw materials, plant setup, equipment, financial considerations, and regulatory requirements to establish an Alkyl Ether Sulfates manufacturing plant. This report is crucial for investors, entrepreneurs, and manufacturers who are considering entering the surfactant production industry or expanding their existing production capabilities.
Industry Overview
The global surfactants market has experienced substantial growth, driven by increasing consumer demand for personal care products, detergents, and industrial cleaning solutions. Surfactants like Alkyl Ether Sulfates (AES) are one of the most common ingredients in personal care products due to their mildness and effective cleansing properties. AES, especially in the form of sodium lauryl ether sulfate (SLES), is widely used in shampoos, body washes, and other cosmetic products, making it a valuable ingredient in the global market.
Furthermore, the growing demand for eco-friendly, biodegradable, and mild surfactants has resulted in an increased demand for Alkyl Ether Sulfates, as they are considered less irritating compared to other harsher surfactants like sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS). As a result, the market for AES continues to grow in both developed and emerging economies, driven by a rising middle class and increasing awareness of personal care and cleaning products.
The global market for surfactants is expected to continue expanding, providing a significant opportunity for manufacturers to invest in Alkyl Ether Sulfates production. The trend towards sustainability and the use of renewable feedstocks is also shaping the future of the surfactant industry.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
Raw Materials for Alkyl Ether Sulfates Production
The production of Alkyl Ether Sulfates involves the use of several key raw materials, which must meet stringent quality standards to ensure the production of high-quality surfactants.
1. Fatty Alcohols
- Fatty alcohols are the primary raw material used in the production of Alkyl Ether Sulfates. These alcohols, derived from natural fats and oils or petrochemicals, typically contain 12 to 18 carbon atoms and are used as the starting point for the synthesis of AES.
- Lauryl Alcohol (C12) and C14-C16 Alcohols are commonly used for AES production.
- Fatty alcohols can be obtained from renewable sources like palm oil or coconut oil, contributing to the eco-friendly aspect of the production process.
2. Ethanol (Ethylene Oxide)
- Ethanol (ethoxylation agent) is used to ethoxylate the fatty alcohols in a process known as ethoxylation. The ethoxylation reaction attaches ethylene oxide molecules to the fatty alcohols, creating fatty alcohol ethoxylates that are key components in Alkyl Ether Sulfates.
3. Sulfur Trioxide (SO3)
- Sulfur Trioxide is the critical reagent for the sulfation step in the production of Alkyl Ether Sulfates. It reacts with the ethoxylated fatty alcohols to form alkyl ether sulfates.
4. Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH)
- Sodium Hydroxide is used to neutralize the reaction mixture after sulfation to form sodium alkyl ether sulfate.
5. Water
- Water is used in various steps, such as in neutralization and washing, to remove impurities from the final product.
6. Other Additives
- Additives like preservatives, colorants, and fragrances may be used, especially when producing Alkyl Ether Sulfates for personal care applications.
Manufacturing Process
The production of Alkyl Ether Sulfates involves several steps, including ethoxylation, sulfation, neutralization, and finishing. Below is a detailed explanation of each stage of the manufacturing process:
1. Fatty Alcohol Ethoxylation
- Ethoxylation is the first step in the production of Alkyl Ether Sulfates. In this step, fatty alcohols are reacted with ethylene oxide in the presence of a catalyst. The process involves heating the fatty alcohols and ethylene oxide under controlled conditions to form fatty alcohol ethoxylates.
- The ethoxylation reaction creates an intermediate compound, which is the key building block of Alkyl Ether Sulfates. The number of ethylene oxide units attached to the fatty alcohol molecule can be controlled, affecting the final properties of the AES.
2. Sulfation
- Sulfation is the next step, where sulfur trioxide (SO3) is introduced into the reaction mixture. The sulfur trioxide reacts with the ethoxylated fatty alcohols to introduce the sulfate group (-SO3) into the molecular structure, forming Alkyl Ether Sulfates.
- The reaction takes place in a specialized sulfation reactor, where the mixture is kept under controlled temperature and pressure conditions to ensure complete conversion of the ethoxylated alcohol into the sulfate form.
3. Neutralization
- After the sulfation reaction is complete, the reaction mixture is neutralized with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to form sodium alkyl ether sulfate. This neutralization process helps convert the sulfuric acid by-products into water-soluble salts, which can be easily removed.
- The resulting mixture is then thoroughly mixed and diluted with water to wash away any remaining contaminants and by-products from the neutralization process.
4. Purification and Filtration
- The product is then subjected to filtration to remove any insoluble impurities. If necessary, additional washing with water is done to ensure the purity of the Alkyl Ether Sulfate.
- Drying may also be conducted if the final product is to be sold in powder form.
5. Concentration and Drying
- If the desired product is a concentrated liquid or solid form, the solution undergoes further concentration through evaporative techniques to remove excess water. This ensures that the final product meets the required specifications for the market.
6. Blending and Finishing
- Depending on the application, the Alkyl Ether Sulfate is blended with additional ingredients like preservatives, colorants, and fragrances. The final formulation is then tested to meet specific customer requirements and industry standards.
7. Packaging
- After completing all steps, the Alkyl Ether Sulfates are packaged in suitable containers, such as drums, bottles, or bulk tanks, depending on the end-use market. Proper labeling and storage conditions are crucial to maintain the quality and stability of the product.
Plant Setup and Infrastructure
To establish a successful Alkyl Ether Sulfates manufacturing plant, the following infrastructure elements must be taken into account:
1. Location
- The plant should be located in an industrial area with easy access to raw material suppliers, transportation hubs, and key markets for finished products. Proximity to water and waste disposal systems is also important.
2. Factory Layout
- The factory layout should be optimized to ensure efficient production flow. Key sections of the plant include:
- Raw Material Storage Area: For storing fatty alcohols, ethylene oxide, sulfur trioxide, and other raw materials.
- Reaction Area: Where ethoxylation and sulfation reactions take place.
- Neutralization and Washing Area: For neutralizing the reaction mixture and purifying the product.
- Filtration and Drying Area: To remove impurities and excess moisture.
- Packaging Area: For packaging the final product into various forms.
3. Machinery and Equipment
- Key equipment for an Alkyl Ether Sulfates manufacturing plant includes:
- Ethoxylation Reactors: For ethoxylating fatty alcohols.
- Sulfation Reactors: For introducing sulfate groups to the ethoxylated alcohols.
- Neutralization Tanks: For neutralizing the reaction mixture with sodium hydroxide.
- Filtration Units: For purifying the product and removing insoluble impurities.
- Drying Equipment: If solid or concentrated products are desired.
- Packaging Machines: For filling the final product into drums, bottles, or bulk containers.
4. Utilities
- Electricity: For powering machinery, pumps, and reactors.
- Water: Required for neutralization, washing, and cooling processes.
- Steam: Used for heating during ethoxylation and sulfation reactions.
- Compressed Air: For controlling the flow of materials and cleaning.
- Waste Management: Ensuring proper disposal of chemical waste and by-products.
5. Staffing
- Skilled personnel are required to operate machinery, monitor production processes, and conduct quality control. Key staff include:
- Chemical Engineers: To oversee the production process.
- Technicians: For operating reactors and other equipment.
- Quality Control Analysts: For testing raw materials, in-process samples, and finished products.
- Maintenance Personnel: To ensure the smooth operation of machinery and equipment.
- Administrative and Sales Staff: To manage logistics, inventory, and customer relations.
Cost Analysis and Financial Planning
Setting up an Alkyl Ether Sulfates manufacturing plant requires significant investment. Below is an outline of the major cost components:
1. Capital Investment
- Land and Infrastructure: Costs for purchasing or leasing land and constructing the plant.
- Machinery and Equipment: Investment in reactors, neutralization tanks, filtration units, drying equipment, and packaging machines.
- Raw Materials: Initial purchase of fatty alcohols, ethylene oxide, sulfur trioxide, and other chemicals.
2. Operational Costs
- Raw Materials: Ongoing costs for purchasing fatty alcohols, ethylene oxide, sulfur trioxide, and other chemicals.
- Labor Costs: Salaries for production workers, quality control personnel, engineers, and administrative staff.
- Utilities: Costs for electricity, water, steam, and waste management.
3. Regulatory Compliance Costs
- Compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and other regulatory standards requires investment in safety, quality control, and environmental monitoring systems.
4. Marketing and Distribution
- Marketing: Budget for advertising and promoting the product in target markets.
- Transportation: Costs for distributing the finished product to local or international customers.
5. Profitability
- With increasing global demand for personal care and household cleaning products, the profitability of the plant depends on efficient operations, market positioning, and maintaining high product quality. The return on investment (ROI) can be significant with careful planning and execution.
Regulatory Considerations
The production of Alkyl Ether Sulfates is subject to various environmental, safety, and quality regulations, including:
- Environmental Regulations: Managing chemical waste and emissions during the production process.
- Health and Safety Regulations: Ensuring worker safety during the handling of chemicals like sulfur trioxide.
- Product Quality Standards: Ensuring that the final product complies with industry standards for surfactants, such as ISO and GMP guidelines.